The SESAM - System: Difference between revisions
From Ameise-en
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
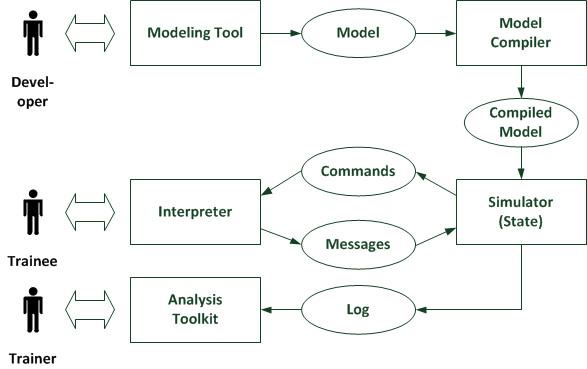
===The Structure of the SESAM - System=== | ===The Structure of the SESAM - System=== | ||
The main objective of using SESAM is an almost realistic simulation of software projects for training purposes. Students should be able to apply their acquired knowledge playfully and depend it on base of | The main objective of using SESAM is an almost realistic simulation of software projects for training purposes. Students should be able to apply their acquired knowledge playfully and depend it on base of a simulation run. | ||
Another aim is to make it possible to model unsecured hypotheses and study their consequences by replaying | Another aim is to make it possible to model unsecured hypotheses and study their consequences by replaying a simulation run. The SESAM - System is built of various ''' Components ''', which are used by different roles: | ||
* '''Modeler''': | * '''Modeler''': | ||
** He creates substantial empirical models that are simulated by the base machine. He determines which objects and relationships of a software project are mapped and what effects may occur. He | ** He creates substantial empirical models that are simulated by the base machine. He determines which objects and relationships of a software project are mapped and what effects may occur. He defines the world in which the trainee is able to move. | ||
* '''Trainee''': | * '''Trainee''': | ||
** The trainee takes the role of the project manager. He intervenes via commands in the course of | ** The trainee takes the role of the project manager. He intervenes via commands in the course of a simulation run and receives messages about the current state from the system. | ||
* '''Instructor''': | * '''Instructor''': | ||
** The instructor conducts training courses, where trainees are able to participate. He lead trainees and he has the possibility to analyze | ** The instructor conducts training courses, where trainees are able to participate. He lead trainees and he has the possibility to analyze simulation runs through evaluation tools, to discuss the achieved results with the trainees. | ||
The following figure shows the ''' | The following figure shows the '''Roles ''' and their '''Interaction ''' with the components of the system. | ||
[[Image:Komponenten_en.gif|center|frame|Components and Roles of the SESAM - System]] | [[Image:Komponenten_en.gif|center|frame|Components and Roles of the SESAM - System]] | ||
Revision as of 21:35, 9 May 2013
The Structure of the SESAM - System
The main objective of using SESAM is an almost realistic simulation of software projects for training purposes. Students should be able to apply their acquired knowledge playfully and depend it on base of a simulation run.
Another aim is to make it possible to model unsecured hypotheses and study their consequences by replaying a simulation run. The SESAM - System is built of various Components , which are used by different roles:
- Modeler:
- He creates substantial empirical models that are simulated by the base machine. He determines which objects and relationships of a software project are mapped and what effects may occur. He defines the world in which the trainee is able to move.
- Trainee:
- The trainee takes the role of the project manager. He intervenes via commands in the course of a simulation run and receives messages about the current state from the system.
- Instructor:
- The instructor conducts training courses, where trainees are able to participate. He lead trainees and he has the possibility to analyze simulation runs through evaluation tools, to discuss the achieved results with the trainees.
The following figure shows the Roles and their Interaction with the components of the system.